
Controls & Transformers
Questions and Answers
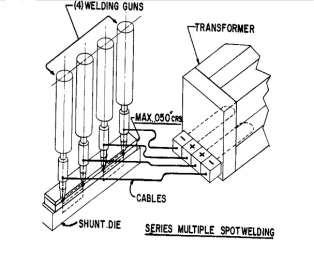
Series welds do have shunting currents as shown in the sketch below. The transformer is attached to weld guns both on the same side of the part and the current must flow through the shunting die or part to return to the transformer. Some amount of current will flow across the top sheet unless this distance is large which would increase the resistance and retard this flow. Any current flow in the top sheet is wasted current "shunting current" that does not contribute to the weld nugget. This type of tooling arrangement is used when access to the underside of the part is restricted.
In North America, Europe and many other parts of the world AC power is frequently converted into DC at 1000 Hz. This is referred to as MFDC which stands for MID FREQUENCY DIRECT CURRENT. In some parts of the world AC is converted to DC single phase and others to DC at various frequencies higher and lower than 1000Hz. One such MFDC example is DC at 600 Hz.
The general rule of thumb is to turn the water off when you turn the power off and in turn the water should be turned back on when the machine is powered up again.
See Article: “When Should the Cooling Water be Turned On?”
If the chiller remains on during a machine off period, it may be fine provided that there are no water leaks and condensation does not accumulate anywhere on the machine. This can be critical in the SCR, the electronics of the controls and the transformer. Condensation on or in any of these components can lead to a short and failure of the SCR, Transformer or Control.
So the question might be how cold is the chilled water? What is the ambient humidity? How long will the machine be idle? Are there hose leaks that normally are dried up by the equipment operation? If any of these answers would indicate water accumulation then shut the chiller down and protect the equipment.
If the water was left on during the down time and water did not accumulate on any surfaces today the gamble paid off and you should be able to turn the machine back on and operate again.
Remember the recommended method to protect the SCR’s, Control and Transformers is:

References: AWS Standard J1.2M/J1.2:2016 "Guide to Installation and Maintenance of Resistance Welding Machines"
RWMA Manual Fourth Edition
A multiple spot or multi-spot transformer is frequently referred to as a fixture type transformer. Multiple spot transformers are frequently used in spot welding fixtures. These AC transformers run from 20 to 200 KVA. They can be built with outputs for either one or two secondary circuits. The secondary’s will fire together with the same power and settings sent from the weld control.
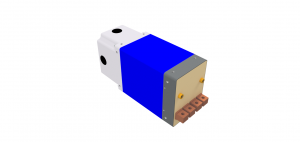
Multiple Spot Transformer with two Secondary’s
Machine transformers vary in size from small 20 KVA to large 500 KVA, AC units. These water cooled stacked core transformers are ideal for press, seam and rocker arm welders.
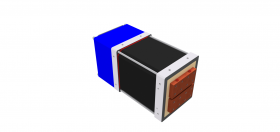
RWMA Size 3 Machine Transformer
These transformers frequently have tap switches to expand the power options.
Page 17 of 40
Have a Question?
Do you have a question that is not covered in our knowledgebase? Do you have questions regarding the above article? Click here to ask the professor.
